Centralized Maintenance Management Platform
Metro rail operations were being run on fragmented, siloed systems for assets, inventory, failures, and workforce management. These systems did not communicate with each other, which meant that teams lacked contextual visibility into the overall maintenance environment. As a result, coordination across departments was slow and error-prone, leading to reactive maintenance and costly downtime. Opportunities for optimization were hidden because data was trapped in silos, and the maintenance function was perceived as a cost center rather than a contributor to value creation.
Solution
I led the end-to-end rollout of a centralized CMMS that unified all asset, inventory, failure, and workforce data into a single platform. This new system digitized thousands of assets into a hierarchical registry and integrated SCADA telemetry streams to automate job-card generation and scheduling. Work orders that had once required manual coordination across multiple departments were now auto-generated, auto-assigned, and tracked through their full lifecycle. The platform also introduced real-time dashboards that gave leadership visibility into KPIs such as Mean Time to Repair (MTTR), Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), asset uptime, and technician performance. This allowed operations to move from reactive and preventive maintenance workflows to predictive and condition-based approaches.
Impact
The transformation reduced downtime incidents across the metro network, unlocking multimillion-dollar annual savings. The single source of truth improved efficiency across operations and enabled leadership to manage performance proactively. By implementing telemetry-driven scheduling and automated inventory orchestration, the platform not only improved system uptime by more than 40 percent but also reduced inventory working capital costs by 70 percent. Most importantly, maintenance shifted from being a cost center to becoming a measurable value driver for the organization.
Technical Highlights
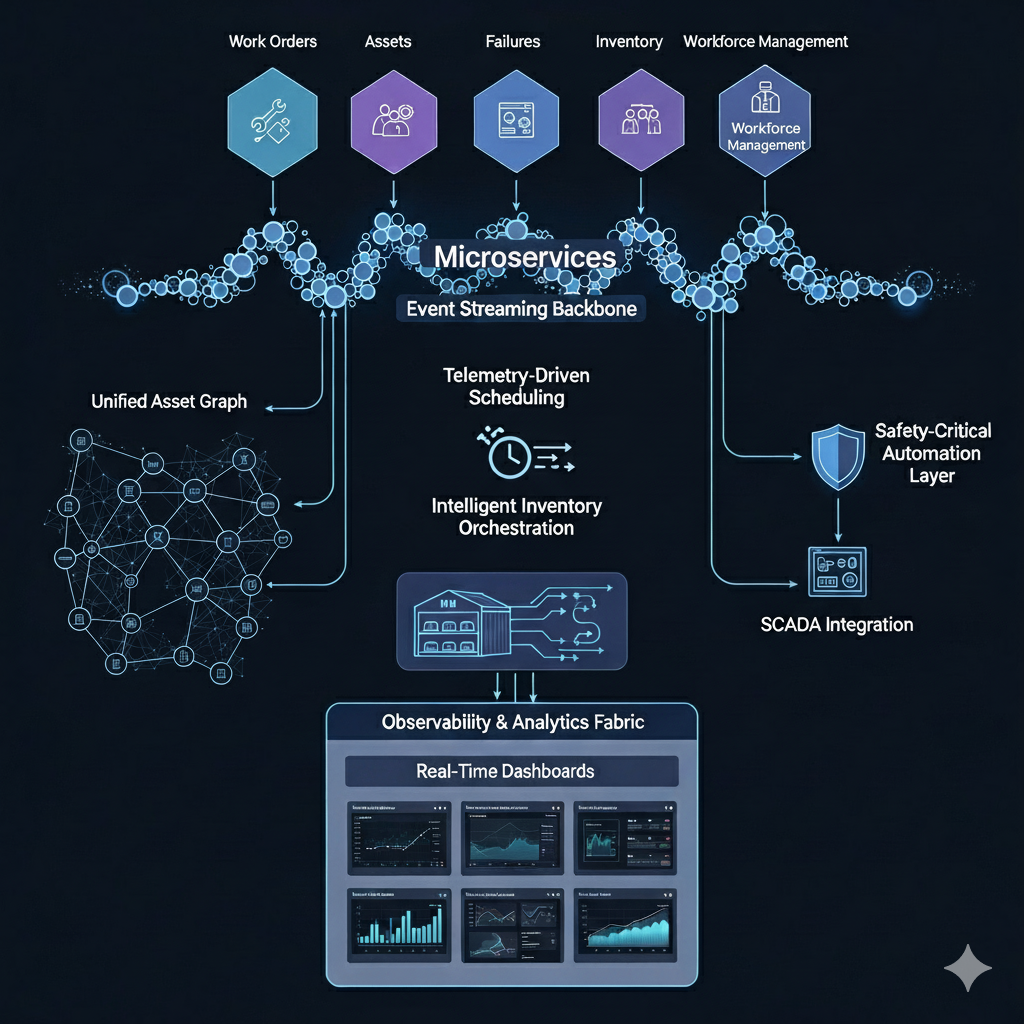
- Event-driven microservices architecture: Designed on modular, event-driven principles with loosely coupled services for work orders, assets, failures, inventory, and workforce management.
- Unified asset graph: Implemented a hierarchical asset registry (digital twin–like structure) to model 2,000+ assets and subcomponents, enabling automated checklists, safety workflows, and SCADA integration.
- Telemetry-driven scheduling: Work order engine ingested asset telemetry, historical maintenance logs, and rule-based policies to dynamically generate job cards with predicted inventory, tools, and labor allocation.
- Intelligent inventory orchestration: Real-time inventory allocation engine synchronized with 17+ vendor APIs, applied consumption forecasting, and auto-blocked parts to ensure availability at execution.
- Safety-critical automation layer: Integrated directly with SCADA for automated block enablement/cancellation, enforcing compliance before maintenance steps could proceed.
- Event streaming backbone: Domain modules communicated via message queues and enrichment engines, supporting low-latency updates and horizontal scalability across thousands of concurrent work orders.
- Observability & analytics fabric: Real-time dashboards tracked MTTR, MTBF, uptime/downtime trends, inventory burn rates, and technician performance, powered by unified data pipelines.